II. HR Management
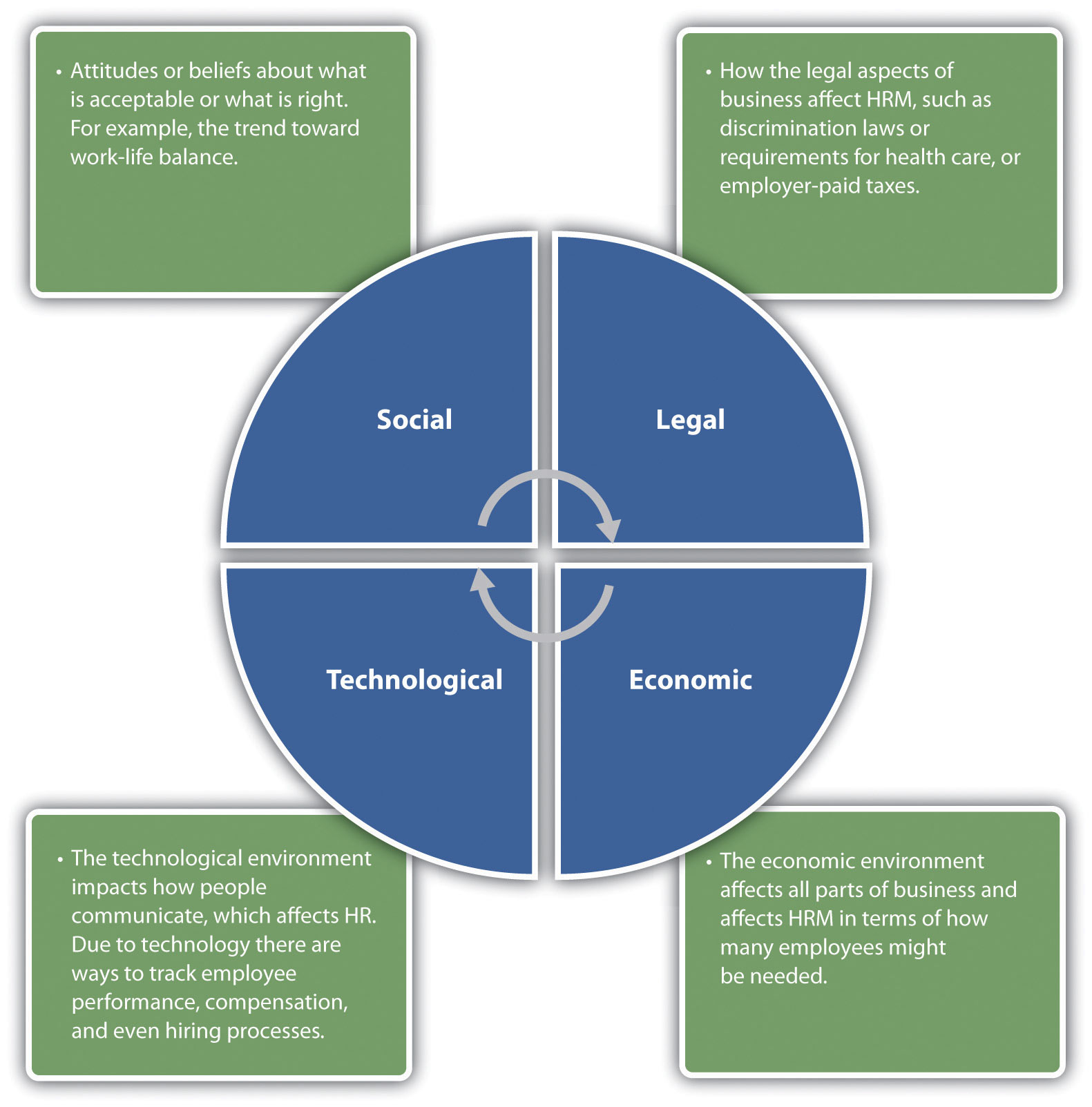
Human asset (HR) the executives alludes to the most common way of overseeing HR, including workers, to amplify their true capacity and efficiency while guaranteeing consistence with regulations and guidelines. HR the board includes a scope of capabilities, including enrolling, recruiting, preparing, pay and advantages, representative relations, and execution the executives.
A portion of the vital areas of HR the executives include:
1. Recruitment and determination: Finding and employing qualified possibility to fill work opening.
2. Training and advancement: Furnishing workers with the abilities and information they need to play out their positions actually and to foster their professions.
3. Performance administration: Defining execution objectives and goals, leading execution evaluations, and giving criticism to representatives to further develop execution.
4. Compensation and advantages: Creating and directing compensation and advantages programs that draw in and hold representatives.
5. Employee relations: Overseeing worker relations issues like debates, complaints, and disciplinary activities.
6. Compliance: Guaranteeing consistence with regulations and guidelines connected with business, like equivalent business opportunity, work environment wellbeing, and work regulations.
Generally, powerful HR the board is basic to the outcome of an association. It assists with guaranteeing that workers are roused, drew in, and useful, which can prompt expanded benefit and seriousness in the commercial center.
Role of Human Resource Management in Organizational Performance
The job of Human Asset The executives (HRM) in hierarchical execution is pivotal as it guarantees that an association has a skillful and useful labor force. HRM centers around overseeing representatives really and productively to expand their true capacity and increment efficiency. HRM adds to authoritative execution in more ways than one:
1. Recruitment and determination: HRM is liable for drawing in and choosing the right workers for the association. This guarantees that the association has a gifted and talented labor force that can drive hierarchical achievement.
2. Training and improvement: HRM is liable for recognizing preparing and advancement needs and giving the vital preparation and advancement projects to assist representatives with upgrading their abilities and information. This guarantees that representatives are furnished with the essential abilities to complete their work works proficiently and actually.
3. Performance administration: HRM is liable for laying out execution objectives, giving input, and assessing representative execution. This guarantees that workers know about their exhibition assumptions and are inspired to accomplish them.
4. Compensation and advantages: HRM is answerable for setting pay and arrangement for assistance that are cutthroat and lined up with industry principles. This guarantees that workers are persuaded to remain with the association and are compensated for their exhibition.
5. Employee relations: HRM is liable for establishing a positive workplace that cultivates worker commitment and maintenance. This guarantees that representatives are happy with their work and are spurred to add to the association’s prosperity.
Generally, HRM assumes a basic part in hierarchical presentation by guaranteeing that the association has a skillful, drew in, and useful labor force that can drive hierarchical achievement.
Functions of HRM
Human Asset The board (HRM) is liable for dealing with the human resources in an association. The elements of HRM include:
1. Recruitment and choice: HRM is answerable for drawing in, choosing, and recruiting the best-fit contender for the association. This includes making sets of responsibilities, posting position opportunities, screening resumes, leading meetings, and choosing the most appropriate applicants.
2. Training and advancement: HRM is answerable for planning and carrying out preparing programs for representatives to improve their abilities and information. This includes recognizing preparing needs, making preparing plans, choosing coaches, and assessing the adequacy of the preparation programs.
3. Performance administration: HRM is answerable for dealing with the presentation of workers. This includes laying out execution objectives, giving input, leading execution assessments, and creating execution improvement plans.
4. Compensation and advantages: HRM is answerable for planning and carrying out remuneration and advantages programs. This includes deciding pay rates, rewards, and different motivations, as well as choosing and overseeing representative advantages, for example, medical coverage and retirement plans.
5. Employee relations: HRM is answerable for overseeing representative relations. This includes making and carrying out strategies and techniques, taking care of complaints and questions, and guaranteeing consistence with work regulations and guidelines.
6. Safety and wellbeing: HRM is answerable for guaranteeing the security and strength of workers. This includes making and carrying out security arrangements and techniques, giving wellbeing preparing, and guaranteeing consistence with security regulations and guidelines.
7. Human asset data frameworks: HRM is answerable for overseeing human asset data frameworks (HRIS). This includes choosing and carrying out HRIS, overseeing representative information, and utilizing HRIS to help other HR capabilities.
Process and Methods of Job Analysis
Work investigation is the methodical course of social event and examining data about a task. It includes gathering information about the obligations, obligations, abilities, and necessities of a specific work. The motivation behind work investigation is to give exact data about a task so associations can settle on informed conclusions about enlistment, preparing, remuneration, and other human asset the board exercises. Coming up next are the means associated with the cycle and strategies for work examination:
1. Identify the reason and extent of the gig examination: The most important phase in work investigation is to distinguish the reason and extent of the investigation. This includes deciding why the work examination is being led and which occupations will be broke down.
2. Collect information: The subsequent stage is to gather information about the gig. Information can be gathered through different strategies like perception, interview, poll, and work journal. The information gathered ought to cover different parts of the gig, for example, work obligations, obligations, abilities required, gear utilized, working circumstances, and actual requests.
3. Analyze the information: When the information has been gathered, it should be dissected to distinguish the key work prerequisites and obligations. This should be possible through satisfied investigation, task examination, and basic episode strategy.
4. Validate the investigation: The work examination should be approved to guarantee that it is precise and dependable. This should be possible through work perceptions, interviews with managers and representatives, and audit of sets of responsibilities.
5. Document the outcomes: The consequences of the gig examination should be recorded in an unmistakable and brief way. This should be possible through the making of an expected set of responsibilities or a task particular.
6. Use the outcomes: The last move toward the gig investigation process is to utilize the outcomes to illuminate human asset the board exercises like enlistment, determination, preparing, and execution assessment.
In outline, work examination is a fundamental cycle for associations to guarantee that they have exact and cutting-edge data about their positions. The interaction includes gathering information, dissecting it, approving the investigation, recording the outcomes, and utilizing the outcomes to illuminate human asset the board exercises.
Planning and Forecasting Personnel Needs
Arranging and determining faculty needs is a urgent part of human asset the board. It includes breaking down the current and future labor force requirements of an association and creating systems to address those issues. Coming up next are the means engaged with arranging and estimating faculty needs:
1. Conduct a labor force examination: The initial step is to lead a labor force investigation to decide the ongoing labor force status of the association. This includes dissecting the quantity of representatives, their abilities, information, and capacities, and their work jobs and obligations.
2. Analyze business technique: The subsequent stage is to examine the business procedure of the association. This includes grasping the objectives, targets, and vision of the association and how they connect with the labor force.
3. Identify future labor force needs: In light of the labor force examination and business procedure, the subsequent stage is to distinguish future labor force needs. This includes distinguishing the abilities, information, and capacities that will be expected from here on out and the quantity of workers expected to accomplish hierarchical objectives.
4. Develop enrollment methodologies: The subsequent stage is to foster enlistment techniques to draw in and hold the right ability. This includes distinguishing wellsprings of expected workers and creating enlistment missions to draw in them.
5. Develop maintenance techniques: Whenever workers are recruited, it is vital to foster maintenance procedures to keep them drew in and roused. This includes creating representative commitment programs, profession advancement programs, and different motivations.
6. Monitor and assess: At long last, it is essential to screen and assess the viability of staff arranging and estimating. This includes following the headway of the labor force plan and making changes on a case by case basis.
In outline, arranging and estimating faculty needs is a basic part of human asset the executives. It includes directing a labor force examination, investigating the business technique, recognizing future labor force needs, creating enlistment and maintenance systems, and checking and assessing the viability of the arrangement. By following these means, associations can guarantee that they have the right ability set up to accomplish their objectives and targets.
Recruitment and Selection
Enlistment and determination are significant elements of human asset the executives that include distinguishing and employing the right possibility for the right positions. Coming up next are the means engaged with enlistment and choice:
1. Identify work opportunities: The most vital phase in enlistment and determination is to distinguish work opening in the association. This should be possible through investigating labor force necessities and turnover rates.
2. Develop an expected set of responsibilities: The subsequent stage is to foster an expected set of responsibilities that obviously frames the obligations, obligations, capabilities, and abilities expected for the gig.
3. Develop an enlistment technique: When the set of working responsibilities has been created, the subsequent stage is to foster an enrollment methodology. This includes distinguishing possible wellsprings of competitors and creating enrollment missions to draw in them.
4. Screen resumes and applications: The subsequent stage is to screen resumes and applications to distinguish the most reasonable competitors. This should be possible through surveying resumes and leading introductory meetings.
5. Conduct meetings: When reasonable applicants have been recognized, the subsequent stage is to direct meetings to survey their abilities, information, and capacities. This should be possible through organized interviews, conduct meetings, or board interviews.
6. Conduct personal investigations: Prior to making a proposition for employment, it is vital to direct historical verifications to guarantee that the competitor has a spotless record and is reasonable for the gig.
7. Make a proposition for employment: When the individual verifications have been finished, a proposition for employment can be made to the up-and-comer. This proposition ought to incorporate insights regarding the work, pay, advantages, and begin date.
8. Onboarding and direction: The last move toward enrollment and determination is to installed and situate the new representative to the association. This includes furnishing them with data about the organization culture, approaches, and systems, and guaranteeing that they have the fundamental assets to play out their work.
In rundown, enrollment and determination include recognizing position opening, fostering a set of working responsibilities, fostering an enlistment system, screening resumes and applications, directing meetings, leading record verifications, making a bid for employment, and onboarding and direction. By following these means, associations can guarantee that they are employing the right possibility for the right positions.
Performance Management and Appraisal: Methods and Processes
Execution the executives and examination are basic parts of human asset the board that include assessing the presentation of representatives and giving criticism on their exhibition. Coming up next are the techniques and cycles engaged with execution the board and examination:
1. Setting execution objectives and targets: The most important phase in execution the board and examination is to laid out execution objectives and goals. This includes characterizing the work liabilities and execution assumptions for every representative.
2. Providing continuous criticism: All through the presentation period, giving continuous input to representatives on their performance is significant. This should be possible through normal registrations, instructing, and tutoring.
3. Conducting a proper execution examination: Toward the finish of the exhibition time frame, a conventional presentation evaluation ought to be directed. This includes thinking about the worker’s presentation in contrast to the laid out objectives and goals.
4. Using execution evaluation strategies: There are a few exhibition examination techniques that can be utilized, including the realistic rating scale, basic episode strategy, social perception scale, and 360-degree input.
5. Developing an exhibition improvement plan: In the event that a worker’s presentation is underneath assumptions, a presentation improvement plan ought to be created. This plan frames explicit advances that the worker can take to work on their exhibition.
6. Linking execution to prizes and acknowledgment: Execution ought to be connected to prizes and acknowledgment. This should be possible through execution based pay, advancements, and different types of acknowledgment.
7. Monitoring and assessing the presentation the board framework: It is vital to screen and assess the adequacy of the exhibition the executives framework to guarantee that it is accomplishing its targets. This should be possible through representative reviews and other input components.
In rundown, execution the board and examination include putting forth execution objectives and goals, giving continuous criticism, directing a conventional execution examination, utilizing execution examination strategies, fostering an exhibition improvement plan, connecting execution to prizes and acknowledgment, and checking and assessing the presentation the executives framework. By following these techniques and cycles, associations can guarantee that they are really overseeing and assessing worker execution.
Establishing Strategic Pay Plans
Laying out essential compensation plans is a significant part of human asset the board that includes planning a pay system that lines up with the association’s general business methodology. Coming up next are the means associated with laying out essential compensation plans:
1. Conduct a task examination: The most important phase in laying out an essential compensation plan is to direct a task investigation to decide the abilities, information, and capacities expected for each work in the association.
2. Develop a task assessment framework: When the work investigation has been directed, the subsequent stage is to foster a task assessment framework that relegates a relative worth to each occupation in light of its intricacy, obligation, and different elements.
3. Conduct a market examination: The following stage is to direct a market investigation to decide the common compensation rates for each work in the association.
4. Develop a compensation structure: In light of the gig assessment and market examination, the following stage is to foster a compensation structure that sets the compensation ranges for each work in the association.
5. Determine individual compensation rates: When the compensation structure has been created, individual compensation rates can be resolved in light of elements like execution, experience, and schooling.
6. Implement the compensation plan: The following stage is to execute the compensation plan by imparting the new compensation design and individual compensation rates to representatives and giving preparation to directors and managers on the most proficient method to utilize the new compensation framework.
7. Monitor and assess the compensation plan: The last step is to screen and assess the viability of the compensation intend to guarantee that it is accomplishing its goals. This should be possible through representative studies and other input instruments.
In rundown, laying out essential compensation plans includes directing a task examination, fostering a task assessment framework, leading a market examination, fostering a compensation structure, deciding individual compensation rates, carrying out the compensation plan, and checking and assessing its viability. By following these means, associations can guarantee that their remuneration technique is lined up with their general business methodology and supports their capacity to draw in and hold top ability.
Compensation and Benefits
Remuneration and advantages are basic parts of human asset the board that include planning and executing an all out remunerations program that draws in, rouses, and holds workers. Coming up next are the vital parts of remuneration and advantages:
1. Base compensation: This alludes to the proper compensation or hourly rate that a representative gets for their work.
2. Incentive compensation: This alludes to pay that is attached to individual or group execution, for example, rewards, commissions, and benefit sharing.
3. Benefits: This incorporates non-monetary compensations, for example, medical coverage, retirement plans, took care of time, and different types of representative advantages.
4. Equity remuneration: This alludes to the issuance of investment opportunities, limited stock units, and different types of value to representatives as a component of their pay bundle.
5. Executive remuneration: This alludes to the pay bundles gave to top chiefs in the association, which frequently incorporate a blend of base compensation, impetuses, value pay, and different advantages.
6. Pay straightforwardness: This includes imparting the remuneration reasoning and pay design to representatives and furnishing them with data on how their not set in stone.
7. Compliance: This includes guaranteeing that the remuneration and advantages programs consent to every single material regulation and guidelines, for example, the Fair Work Principles Act, the Equivalent Compensation Act, and the Reasonable Consideration Act.
By planning and executing a far reaching pay and advantages program, associations can draw in and hold top ability, propel workers to perform at their best, and accomplish their general business goals.
Ethics, Justice, and Fair Treatment in HR Management
Morals, equity, and fair treatment are basic standards in human asset the executives that guarantee that workers are treated with deference and pride, and that the association works in a moral and socially dependable way. Coming up next are the vital parts of morals, equity, and fair treatment in HR the executives:
1. Code of morals: This is a composed explanation that frames the association’s qualities and moral standards, and gives direction on how representatives ought to act in the working environment.
2. Equal work a valuable open door: This includes guaranteeing that all representatives and occupation candidates are dealt with similarly and without segregation in light of their race, orientation, age, religion, handicap, or other safeguarded qualities.
3. Diversity and consideration: This includes advancing variety and consideration in the work environment and establishing a climate where all representatives feel esteemed and regarded.
4. Employee security: This includes safeguarding the protection of representative data and guaranteeing that it is utilized exclusively for genuine business purposes.
5. Whistleblower insurance: This includes safeguarding representatives who report deceptive or unlawful way of behaving from reprisal or other unfortunate results.
6. Fair treatment: This includes treating all representatives reasonably and reliably, and furnishing them with valuable open doors for improvement and headway in view of their exhibition and capabilities.
7. Social obligation: This includes guaranteeing that the association works in a moral and socially dependable way, and thinks about the effect of its activities on representatives, clients, the local area, and the climate.
By following these standards, associations can make a culture of morals, equity, and fair treatment, which can prompt higher representative spirit, expanded efficiency, and a positive standing locally.
Labor Relations and Collective Bargaining
Work relations and aggregate haggling are basic parts of human asset the board that include dealing with the connection between the association and its representatives and arranging the agreements of work through an association or other aggregate bartering unit. Coming up next are the critical parts of work relations and aggregate bartering:
1. Union getting sorted out: This includes the course of representatives meeting up to frame an association, which addresses their inclinations in talks with the business.
2. Collective haggling: This includes the discussion of an aggregate dealing understanding (CBA) between the association and the business, which sets the agreements of work, including wages, advantages, and working circumstances.
3. Grievance methodology: This includes laying out techniques for settling debates among representatives and the business, which are normally remembered for the CBA.
4. Labor-administration relations: This includes fabricating and keeping a positive connection between the business and the association, which can assist with forestalling debates and guarantee viable correspondence.
5. Labor regulations: This includes conforming to government and state work regulations, for example, the Public Work Relations Act (NLRA) and the Work The executives Relations Act (LMRA), which administer the connection among managers and associations.
6. Strikes and lockouts: This includes the utilization of work stoppages as a haggling instrument, which can be started by either the association (through a strike) or the business (through a lockout).
By successfully overseeing work relations and aggregate haggling, associations can guarantee that they have a useful and positive relationship with their representatives and the association, which can prompt a more drawn in and roused labor force. It can likewise assist with forestalling questions and limit the gamble of work stoppages, which can altogether affect the association’s activities and notoriety.