Q.6 Discuss the development of “Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty” NPT). define its main features and explain its status in present world. 2019
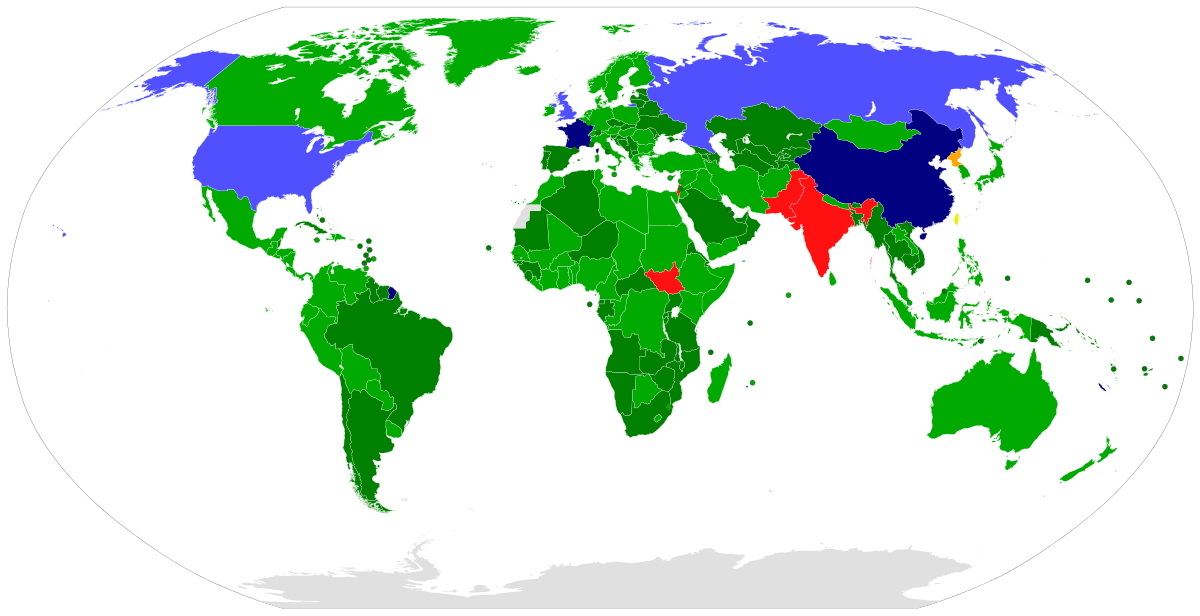
The Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) is a landmark international treaty aimed at preventing the spread of nuclear weapons and promoting disarmament. It was opened for signature in 1968 and entered into force in 1970. The NPT has been signed by 191 countries, making it one of the most widely adopted international treaties in history.
The main features of the NPT include three pillars: non-proliferation, disarmament, and peaceful uses of nuclear energy. Under the non-proliferation pillar, signatory countries agree not to develop or acquire nuclear weapons. Countries that already possess nuclear weapons are recognized as nuclear-weapon states (NWS) and are obligated to work towards disarmament.
The disarmament pillar of the NPT requires NWS to negotiate in good faith towards complete disarmament of their nuclear arsenals. The peaceful uses of nuclear energy pillar ensures that signatories can access nuclear technology and resources for peaceful purposes such as energy production, scientific research, and medicine.
The NPT has played a crucial role in preventing the spread of nuclear weapons. Since the treaty’s inception, only five countries are recognized as NWS: the United States, Russia, China, France, and the United Kingdom. Other countries that had nuclear programs, such as South Africa, Ukraine, and Kazakhstan, have voluntarily dismantled their nuclear weapons programs and joined the NPT as non-nuclear-weapon states (NNWS).
However, the NPT has faced criticism in recent years for its limited progress on disarmament and the potential for loopholes in the treaty that could allow countries to acquire nuclear weapons. Additionally, there are concerns that some countries are using peaceful nuclear energy programs as a cover for developing nuclear weapons.
Despite these challenges, the NPT remains a vital international treaty in promoting nuclear non-proliferation and disarmament. The treaty is regularly reviewed by member states to assess its effectiveness and address emerging issues. The most recent review conference was held in 2015, and the next one is scheduled for 2022.