Q. No. 2. Enumerate the important steps you will follow for completing the Strategic Management Process for a Garment Manufacturing Company.
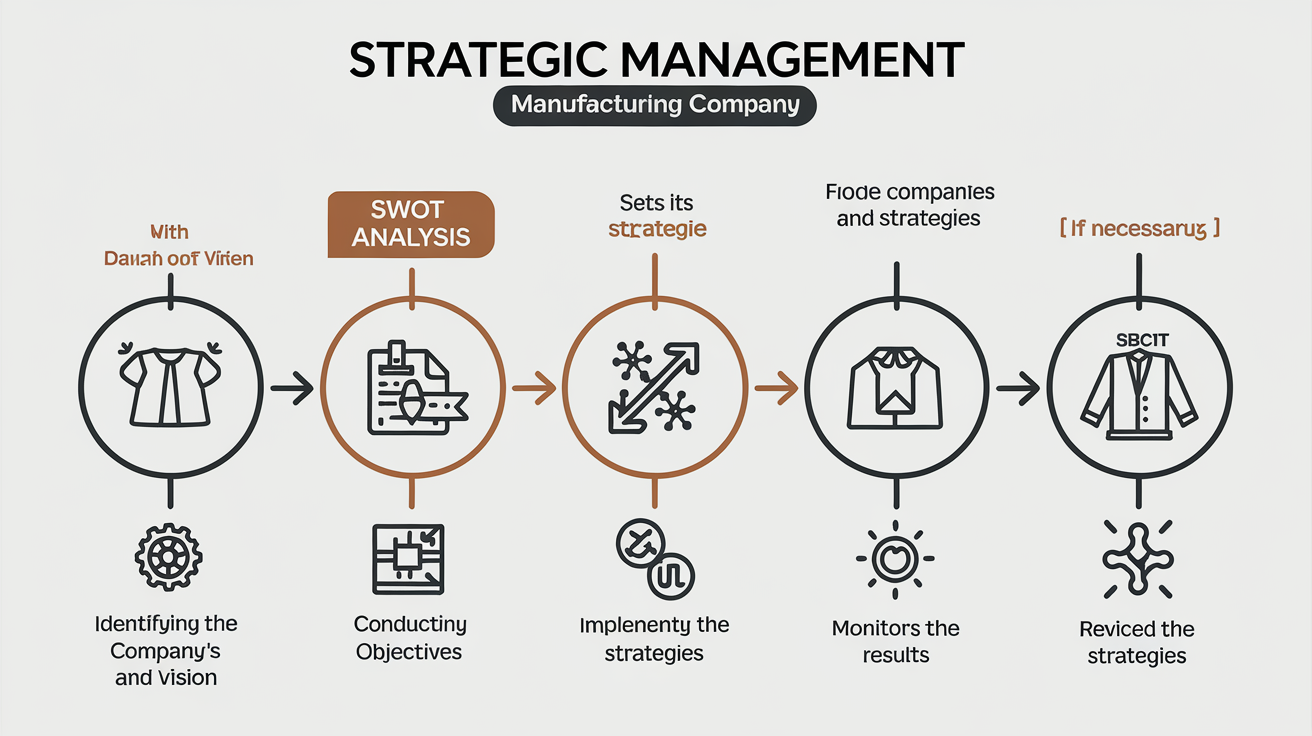
Strategic Management Process for a Garment Manufacturing Company
Strategic management is the process of defining the direction a company will take to achieve its long-term goals. For a garment manufacturing company, this process involves careful planning, resource management, and continuous evaluation to ensure the company remains competitive and can adapt to changes in the market. Here’s a detailed look at the key steps involved:
1. Environmental Analysis (Assessing the Situation)
Before making any strategic decisions, it’s important to fully understand both the company’s internal situation and the external environment it operates in. This involves assessing the company’s strengths and weaknesses, as well as the opportunities and threats from outside.
A. Internal Analysis (Looking Within the Company)
- Resources: Evaluate the company’s resources, such as the skills of the workforce, machinery, finances, and overall operational capabilities. For example, does the company have the right equipment to keep up with modern production techniques?
- Operations: Look at how efficient the current manufacturing processes are. Are there delays or inefficiencies that could be improved?
- Product Range: Assess the company’s product line. Are the products meeting market demand? Are they competitively priced and well-designed?
- Workforce Skills: Review the skill levels of employees and management. Is there enough expertise in areas like garment design, quality control, or sustainability?
B. External Analysis (Understanding the Market)
- Market Trends: Study consumer preferences, such as trends toward sustainable fashion or demand for fast fashion, and how they impact the business.
- Competition: Analyze competitors’ strategies. Are they offering better designs, faster delivery, or lower prices?
- External Influences: Consider external factors such as economic conditions, political stability, and environmental regulations that could impact the business. For instance, new laws about environmental sustainability might require changes in how garments are produced.
2. Strategy Formulation (Deciding on a Plan)
Once you’ve gathered enough information about the internal and external environment, the next step is to develop a clear strategy for the company.
A. Setting Goals
- Vision and Mission: Establish a long-term vision, such as becoming a leader in sustainable garment production, and a mission, like producing high-quality, eco-friendly clothes.
- SMART Objectives: Set specific, measurable goals, such as increasing production by 15% over the next two years or expanding into international markets.
B. Defining the Strategy
- Growth Strategy: Decide how to grow the company. This could be through expanding into new markets, developing new product lines, or improving production processes to reduce costs.
- Competitive Advantage: Identify what will set the company apart from its competitors. This could be offering lower prices through more efficient production, producing unique designs, or focusing on a niche like organic fabrics.
- Local vs. Global Strategy: Decide whether the company should focus on local markets or expand internationally. Global expansion could involve new markets in Europe or Asia, while local strategies may require tailoring products to fit domestic cultural preferences.
3. Strategy Implementation (Putting the Plan into Action)
Having a great strategy is only useful if it is properly executed. Implementation involves turning the plan into concrete actions and making sure the whole organization is aligned with the strategy.
A. Operational Planning
- Detailed Action Plans: Break down strategic goals into actionable steps. For example, if the strategy is to increase production, you’ll need to plan out how to upgrade machinery, train staff, or improve supply chain management.
- Resource Allocation: Make sure resources—money, staff, and technology—are in place to support the plan.
B. Organizational Alignment
- Department Coordination: Ensure that all departments—such as production, sales, and marketing—are working toward the same goals. If the strategy is to launch a new product line, the production team needs to ensure quality, and the marketing team needs to create campaigns that highlight the product’s uniqueness.
- Leadership and Management: Leaders need to communicate the strategy clearly and motivate employees to work toward the company’s goals.
C. Training and Motivation
- Employee Training: Provide necessary training, especially if new technology or production methods are introduced.
- Incentives: Create a system that rewards employees for meeting strategic goals, such as performance bonuses or promotions.
4. Monitoring and Control (Tracking Progress)
Once the strategy is implemented, it’s essential to continuously monitor its success and make adjustments when needed.
A. Performance Measurement
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Set measurable indicators to track success, such as production output, sales growth, or profit margins. For instance, you might track how quickly a new product moves from the factory to retail stores, or how satisfied customers are with the new line.
- Benchmarking: Compare performance against targets regularly to ensure you’re on track.
B. Feedback and Evaluation
- Stakeholder Feedback: Collect input from employees, customers, and suppliers to evaluate whether the strategy is working.
- Balanced Scorecards: Use balanced scorecards to evaluate performance across different areas—financial, customer satisfaction, internal processes, and innovation.
C. Making Adjustments
- If performance isn’t meeting expectations, take corrective actions. For example, if sales of a new product line are lower than expected, review your pricing strategy, product quality, or marketing efforts.
5. Continuous Improvement (Adapting and Evolving)
The strategic management process is ongoing. Even after implementing and monitoring the strategy, there’s always room for improvement.
A. Stay Updated
- Market Trends: Keep an eye on emerging trends in the fashion and garment industry. Whether it’s sustainable fabrics, digital clothing designs, or new customer expectations, staying updated ensures your company remains competitive.
- Innovation: Regularly innovate and improve, whether through new designs, technology, or production processes. Adopting advanced tools like AI for customer insights or digital manufacturing can give your company a competitive edge.
B. Review and Adapt
- Review the company’s strategy periodically to ensure it still aligns with market demands and the company’s long-term goals. If necessary, refine the strategy to meet changing conditions, such as new customer preferences or economic shifts.
Conclusion
The strategic management process for a garment manufacturing company involves careful analysis of both the internal operations and the external market, followed by the development of clear goals and actionable strategies. Successfully implementing those strategies requires aligning all departments, providing the right resources, and continuously monitoring performance. Finally, being adaptable and responsive to changes in the market is key to long-term success.