Q. No. 2. Examine China Strategic Vision behind the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), also known as the One Belt One Road (OBOR) 2021
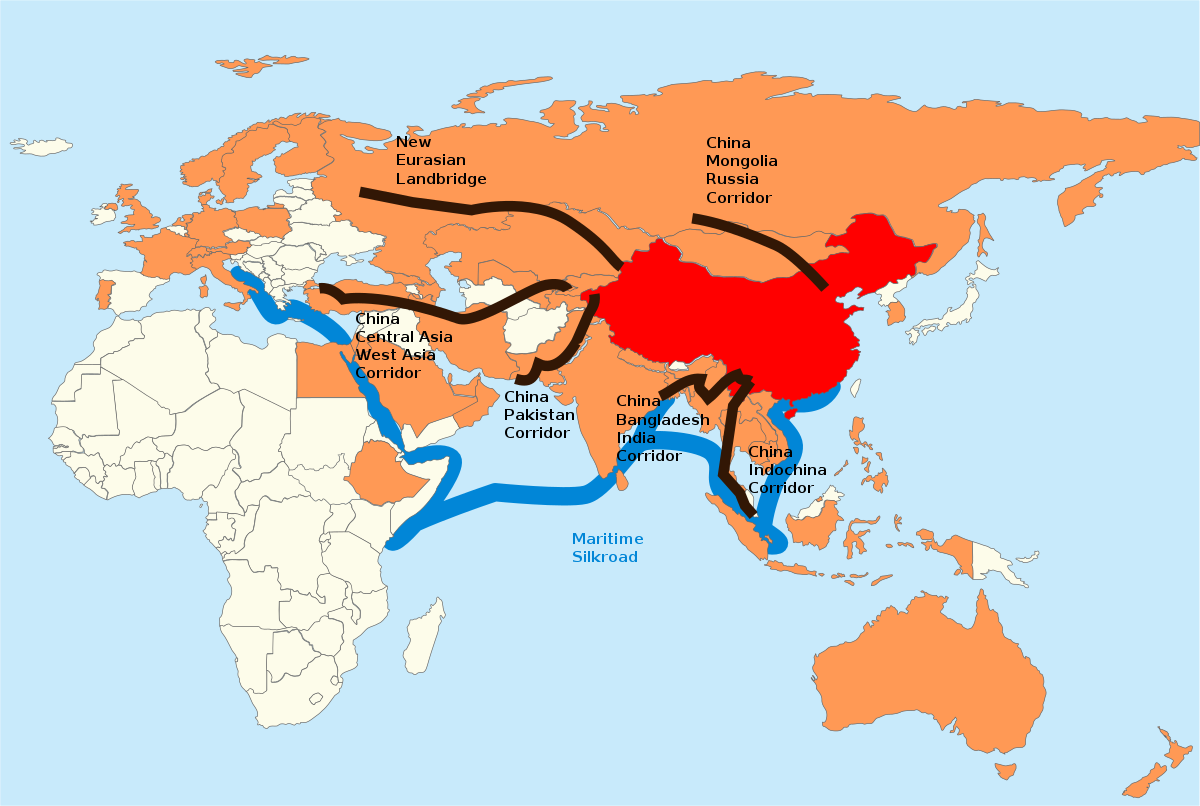
China’s strategic vision behind the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), also known as the One Belt One Road (OBOR), is multi-faceted and encompasses various economic, geopolitical, and developmental objectives. The BRI is a massive infrastructure and connectivity project initiated by China in 2013, aiming to enhance connectivity and promote economic integration across Asia, Europe, Africa, and beyond. Examining China’s strategic vision behind the BRI involves considering several key factors:
- Geopolitical Influence: The BRI allows China to extend its geopolitical influence by building strong economic and diplomatic ties with participating countries. It seeks to position China as a central player in global affairs and enhance its influence in regions traditionally dominated by other powers.
- Economic Expansion: The BRI aims to stimulate economic growth by facilitating trade and investment across participating countries. China, as the world’s second-largest economy, seeks to address its overcapacity in infrastructure and manufacturing sectors by exporting excess production capacity and creating new markets along the BRI routes.
- Energy Security: The BRI promotes the development of energy infrastructure, including pipelines, ports, and power plants, to secure China’s access to vital energy resources. By diversifying energy supply routes and reducing dependency on vulnerable chokepoints, China aims to ensure a stable and uninterrupted flow of energy resources to fuel its growing economy.
- Regional Development and Stability: The BRI aims to promote economic development and alleviate poverty in participating countries, particularly in less-developed regions. By investing in infrastructure projects, China aims to spur economic growth, create employment opportunities, and enhance regional stability, reducing the risk of conflicts and social unrest.
- Cultural Exchanges and People-to-People Connectivity: The BRI emphasizes people-to-people exchanges, cultural cooperation, and educational collaborations. China seeks to strengthen cultural ties, promote mutual understanding, and foster goodwill among participating countries, thereby enhancing its soft power and building stronger diplomatic relationships.
- Internationalization of Chinese Institutions: The BRI provides an opportunity for Chinese financial institutions, such as the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) and the Silk Road Fund, to play a greater role in global finance and infrastructure development. China aims to establish these institutions as alternatives to existing international financial institutions and shape global economic governance in line with its interests.
It is important to note that while the BRI offers potential benefits to participating countries, it has also faced criticism and scrutiny on various fronts, including concerns over debt sustainability, environmental impact, transparency, and geopolitical implications. China’s strategic vision behind the BRI is a complex mix of economic, political, and strategic interests that reflect its aspirations for regional and global influence.