Q3. What are the best policy options to deal with asymmetrical warfare?
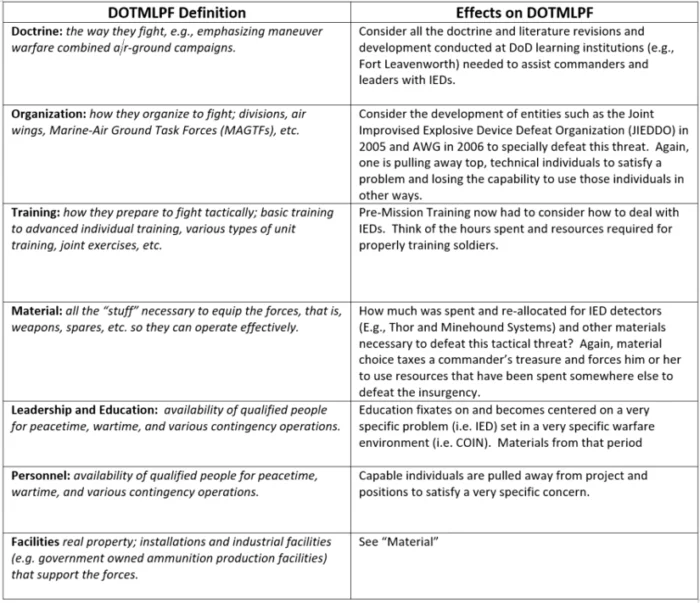
Asymmetrical warfare refers to a type of conflict in which one side has significantly more military power, resources, and technology than the other. Dealing with asymmetrical warfare can be a complex challenge for policy makers, as traditional military strategies may not be effective against non-state actors who use unconventional tactics. Some of the best policy options to deal with asymmetrical warfare include:
- Counterterrorism measures: A key element of any policy response to asymmetrical warfare should be to disrupt and dismantle the organizational and operational capacities of terrorist groups. This can be achieved through the use of intelligence-led operations, including the interdiction of weapons and funding, and the targeting of leaders and key members.
- Diplomatic and political engagement: Diplomatic and political engagement can help address the underlying causes of asymmetrical warfare and build support for an effective policy response. This can involve diplomatic initiatives to resolve conflicts, promote reconciliation, and build partnerships with regional and international actors.
- Capacity building and training: Building the capacities of local security forces and civilian authorities is critical to addressing asymmetrical warfare. This can involve providing training, equipment, and technical assistance to help local actors respond to security threats, improve governance, and support development initiatives.
- Humanitarian assistance: Asymmetrical warfare can often result in large-scale humanitarian crises, and addressing these needs is an important part of any policy response. Humanitarian assistance can help alleviate the suffering of affected populations, promote stability, and build support for a more comprehensive policy response.
- Cybersecurity: In an age of increasing dependence on technology, cybersecurity is becoming an increasingly important aspect of any policy response to asymmetrical warfare. This can involve efforts to protect critical infrastructure, improve information security, and counter the use of technology by non-state actors.
In conclusion, a comprehensive and coordinated policy response to asymmetrical warfare should involve a range of diplomatic, military, development, and security initiatives. The specific policy options that are most appropriate will depend on the specific context and the nature of the asymmetrical threat, and a flexible and adaptive approach will be essential in addressing this complex challenge.